Translate this page into:
Iatrogenic Radial Arteriovenous Fistula Secondary to Transradial Coronary Angiography: A Case Report
Sreekanth Yerram, MD, DM Department of Cardiology, Nizam’s Institute of Medical Sciences, Speciality block 2nd floor, Panjagutta, Hyderabad, Telangana India sreeyerram@gmail.com
This article was originally published by Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Private Ltd. and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Abstract
Transradial access is the commonly followed route for performing percutaneous coronary diagnostic and angioplasty interventions. Transradial access has drastically decreased the vascular access site complications when compared with the transfemoral access. Arteriovenous fistula developing at the transradial access site is one of the rare complications. The risk factors and the mechanism of development are not entirely known. We present a rare case of a 63-year-old female developing radiocephalic fistula a few days after transradial coronary angiography and discuss management.
The transradial route is preferred for cardiovascular interventions. Complications arising out of this are rare even though this route is widely used. Arteriovenous fistula is one of the rare complications, and the mechanisms causing it are not always clearly evident. This report will elaborate on the possible causes and steps to prevent this complication and help in managing once it occurs.
Keywords
transradial
cardiac catheterization
angioplasty
arteriovenous fistula
Introduction
Coronary angiography and interventions are performed via the transradial access, which is gaining rapid popularity and is considered to be the recommended vascular access for coronary interventions. Anatomically, radial artery is a quite a superficial and easily compressible vessel, whereas the femoral vessel is quite deep and difficult to compress and has been proven to decrease the rate of major access site bleeding and mortality.1 In transradial artery (TRA) access, there is an increase in patient comfort, decreased usage of resources, and time for ambulation. Vascular access site complications such as access site hematomas, retroperitoneal hematomas, pseudoaneurysms, arteriovenous fistula (AVF), and arterial dissection are commonly seen at the femoral artery access site than at the radial access site. We, hereby, present a rare case of an iatrogenic AVF, developing as an early complication of transradial diagnostic angiography, whose management is discussed.
Case Report
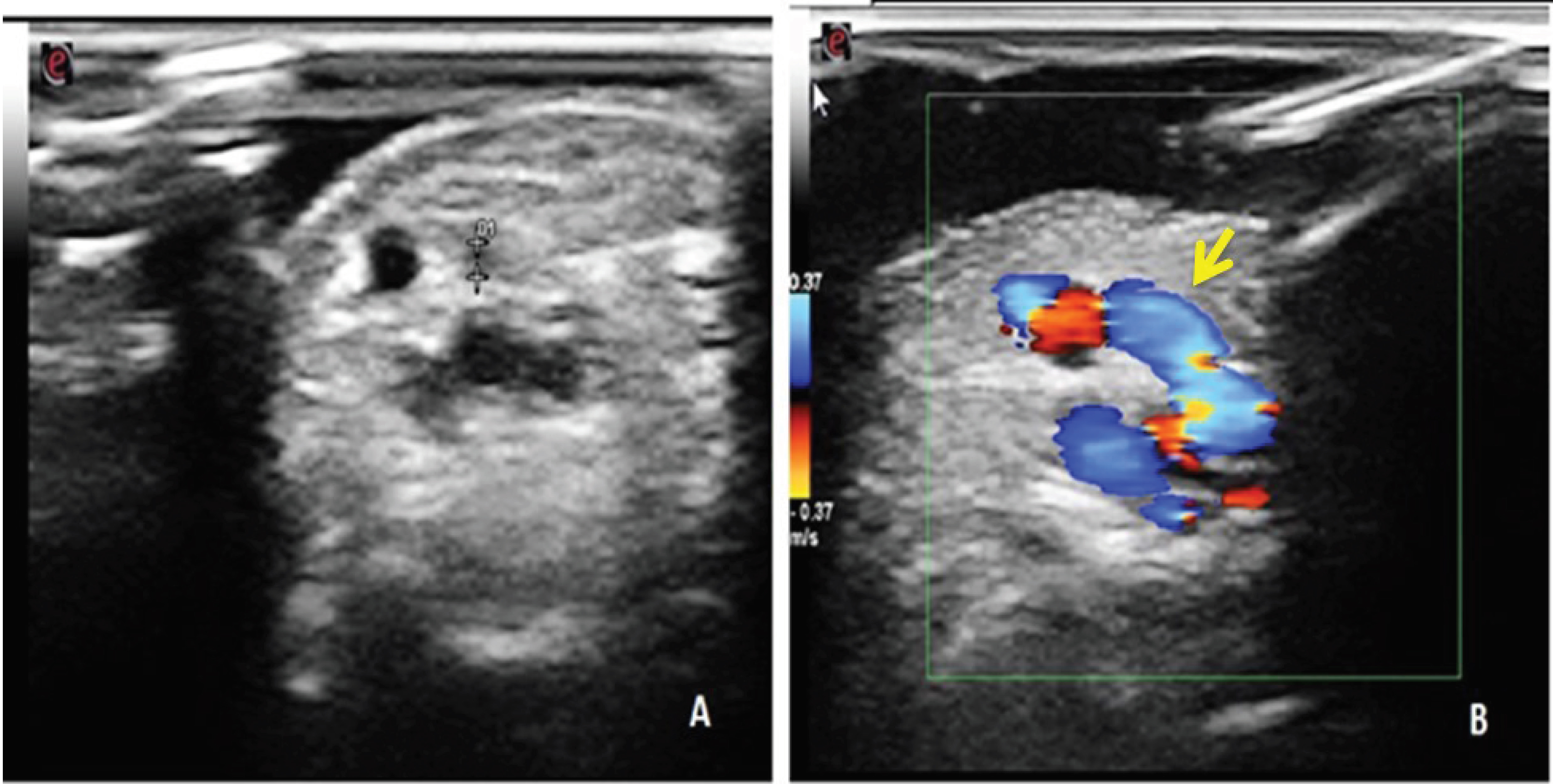
A 63-year-old female known hypertensive for the past 10 years on regular medication presented with chest pain on exertion and shortness of breath over a duration of 4 months. She underwent elective coronary angiography after the stress test was positive for inducible ischemia. A normal Allen's test confirmed dual arterial supply of the palmar arch, and angiography was performed using a 6-French Radifocus Introducer II Transradial Kit - Introducer sheath (Terumo Inc) through the right radial artery access. After completion of angiography, the radial artery sheath was removed immediately and hemostasis was achieved by compressive dressing on the radial artery, which was removed once access site hemostasis was achieved. Palpable thrill was noticed at the right radial puncture site on routine physical examination. Circulatory compromise was not noted on the hand, and the performance of Allen's test remained normal. Color Doppler ultrasound imaging was suggestive of an iatrogenic AVF with turbulent and high-flow velocity at the site of communication. It revealed a fistulous communicating tract between the right radial artery and adjacent subcutaneous vein, which suggested radial arteriovenous fistula (Fig. 1).
-
Fig. 1 Grayscale (A) and Color Doppler (B) ultrasound images, showing an anechoic linear fistulous tract (white arrow) and extending between the radial artery to the cephalic vein at the wrist which shows pulsatile flow.
Fig. 1 Grayscale (A) and Color Doppler (B) ultrasound images, showing an anechoic linear fistulous tract (white arrow) and extending between the radial artery to the cephalic vein at the wrist which shows pulsatile flow.
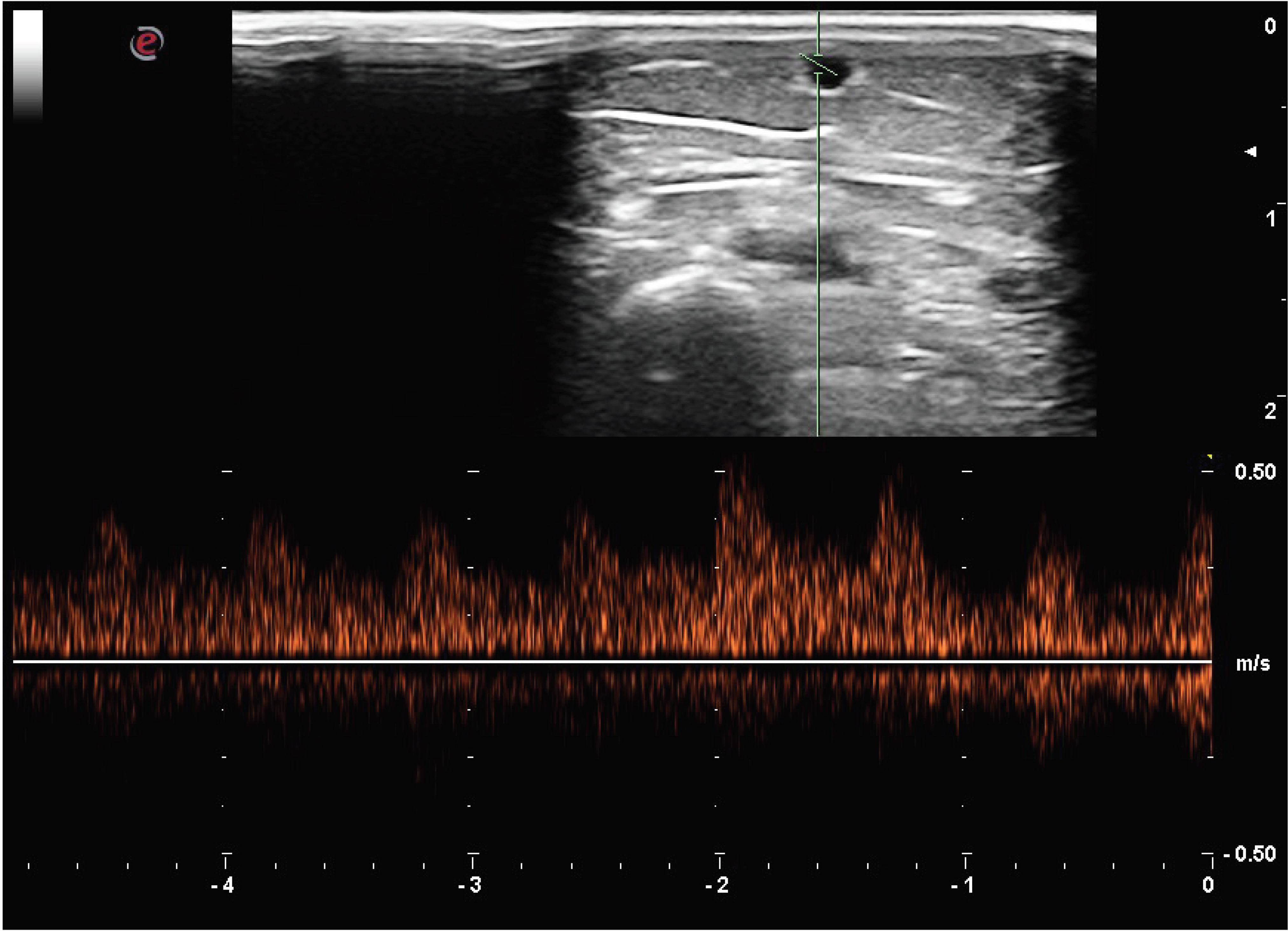
Pulsed wave ultrasound image sampling the cephalic vein in the midforearm, showing arterialized flow (Fig. 2).
-
Fig. 2 Pulsed wave ultrasound image sampling the cephalic vein in midforearm, showing arterialized flow.
Fig. 2 Pulsed wave ultrasound image sampling the cephalic vein in midforearm, showing arterialized flow.
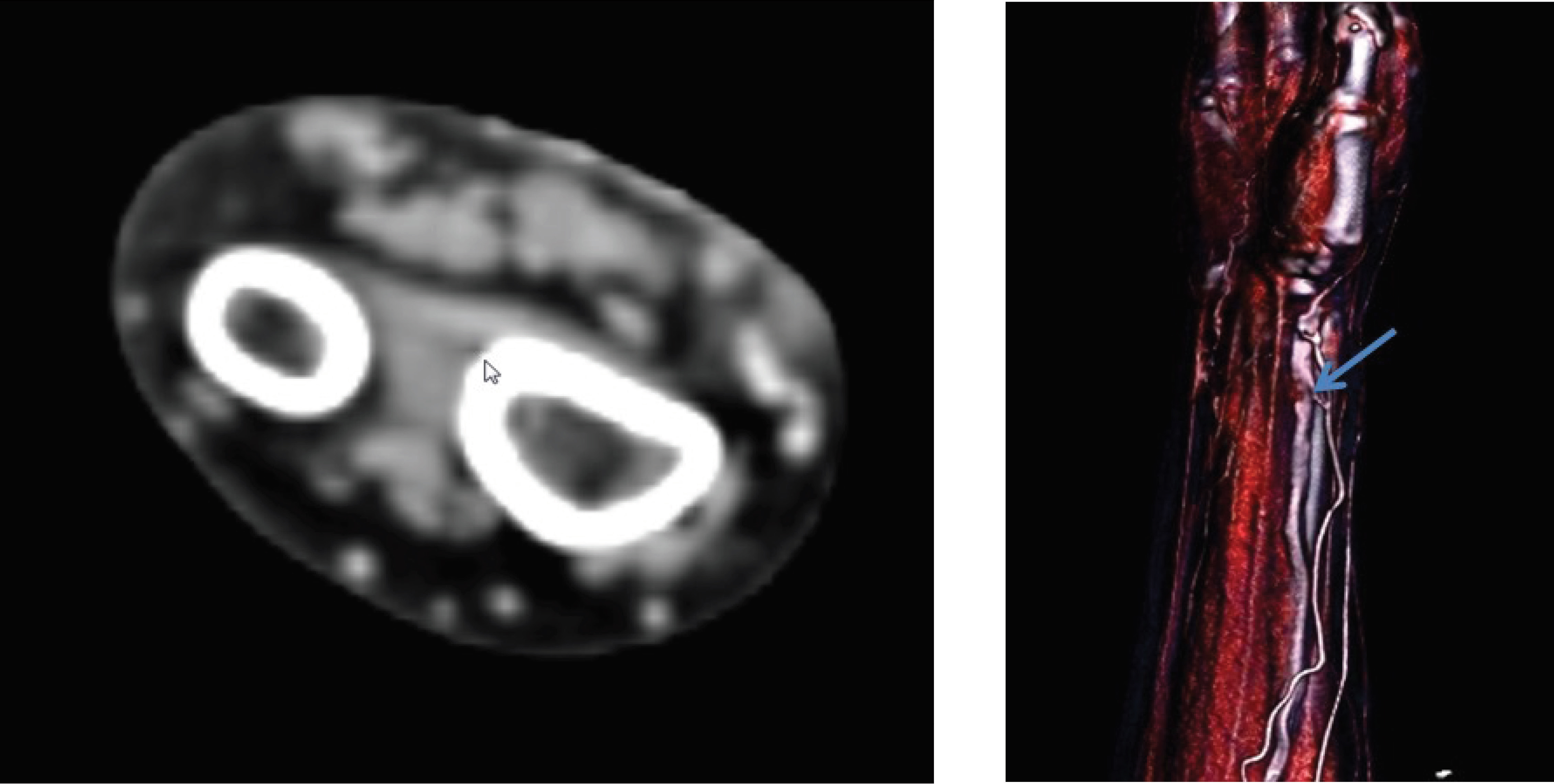
Upper extremity computed tomography (CT) angiography was performed, which is suggestive of fistulous communication between artery and vein, and CT angiogram 3D-shaded surface display images show the small, contrast-filled fistulous tract (white arrow), extending between the radial artery and cephalic vein at the wrist (Fig. 3).
-
Fig. 3 CT angiogram axial (A) and 3D-shaded surface display (B) images, showing the small contrast-filled fistulous tract (white arrow), extending between the radial artery and cephalic vein at the wrist.
Fig. 3 CT angiogram axial (A) and 3D-shaded surface display (B) images, showing the small contrast-filled fistulous tract (white arrow), extending between the radial artery and cephalic vein at the wrist.
Compressive bandage was applied, which resulted in the obliteration of the fistula. The percutaneous intervention was performed through the femoral route.
Discussion
The transradial access site, which is used for coronary interventions, is becoming an increasingly common technique since it was first introduced by Campeau in 1989.2 3 4 A rival study showed that only 5 (0.14%) of the 3514 patients who underwent transfemoral percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) developed AVF, but none of the 3507 patients who underwent transradial artery developed AVF.5 In a large case series of 10,324 patients by Tatli et al, only four cases of AVF were documented, which suggested a very low-incidence of AVF development, complicating transradial coronary angiography.6
Kelm et al7 demonstrated that age above 60 years, female sex, hypertension, prolonged coumadin therapy, and high-heparin dosage during the procedure are the factors which are predisposing for the development of iatrogenic femoral AVFs. These predisposing factors cause delay in the process of healing at punctured artery access sites. Interestingly, other than the female gender, our patient had no other predisposing factors, and her radial artery was accessed after the first puncture. The pathogenesis of iatrogenic AVF is the same in either extremity, upper or lower. Needle deviation during access site puncture through a venous tributary may lead to an unnoticed artery and vein puncture. Almost many of these communications spontaneously seal the artery and vein. However, when there is a persistent communication between the artery and vein, an iatrogenic AVF may form. Iatrogenic AVFs after obtaining transradial access is an infrequently reported complication (0.08%), absence of large veins near the radial artery may be the possible explanation for very low occurence.8
Radial AVF is generally asymptomatic, and it may present with a pulsatile mass, thrill, or bruit heard over the wrist.9 10 Iatrogenic radial AVFs commonly have very smaller shunt volumes, unlike seen in hemodialysis fistulae or large AV fistula, wherein significant hemodynamic changes occur. The time to diagnose AVF is variable, lasting from weeks up to a year after the intervention. Iatrogenic AVF in our patient was identified early after the intervention.
Incidence of iatrogenic AVF can be reduced by decreasing the usage of the same artery multiple times and using smaller arterial sheath when compared with the arterial diameter.
Standard screening modality for patients diagnosed with iatrogenic AVFs is Duplex ultrasonography. CT angiogram usage is gradually increasing because it is minimally invasive, fast, and not dependent on the operator. CT angiography scores by demonstrating the exact spatial relations between the radial artery, superficial veins, and surrounding structures around the AVF, which helps in understanding the mechanism of development of AVF.
The treatment modalities for patients who have persistent iatrogenic AVF are conservative therapy, compression using ultrasound guided probe, placement of a covered stent and, lastly, surgical repair. Mechanical compression resolved 75 percent of the radial AV fistula cases reported by Tatli et al.6
Conclusion
The development of iatrogenic AVF has a very low reported incidence of vascular complications after transradial coronary interventions. Radial AVF is not intervened as long as it is of no inconvenience to the patient, is not enlarging, and not causing any complications; it can be treated conservatively without undergoing any intervention.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Radial versus femoral access for coronary angiography or intervention and the impact on major bleeding and ischemic events: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am Heart J. 2009;157(01):132-140.
- [Google Scholar]
- Percutaneous radial artery approach for coronary angiography. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1989;16:3-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Radial versus femoral approach for percutaneous coronary diagnostic and interventional procedures; Systematic overview and meta-analysis of randomized trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44(02):349-356.
- [Google Scholar]
- A randomized comparison of transradial versus transfemoral approach for coronary angiography and angioplasty. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2009;2(11):1047-1054.
- [Google Scholar]
- RIVAL trial group. Radial versus femoral access for coronary angiography and intervention in patients with acute coronary syndromes (RIVAL): a randomised, parallel group, multicentre trial. Lancet. 2011;377 (9775):1409-1420.
- [Google Scholar]
- Unusual vascular complications associated with transradial coronary procedures among 10,324 patients: case based experience and treatment options. J Interv Cardiol. 2015;28(03):305-312.
- [Google Scholar]
- Incidence and clinical outcome of iatrogenic femoral arteriovenous fistulas: implications for risk stratification and treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40(02):291-297.
- [Google Scholar]
- Vascular complications and access crossover in 10,676 transradial percutaneous coronary procedures. Am Heart J. 2012;163(02):230-238.
- [Google Scholar]
- Rare access site complications following transradial coronary intervention. Can J Cardiol. 2009;25(06):e206.
- [Google Scholar]
- Transradial cardiac catheterization: a review of access site complications. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;78(06):840-846.
- [Google Scholar]








