Translate this page into:
A Case Report of Ortner's Syndrome, Cardiovocal Hoarseness—An Infrequent Entity in the Contemporary World
Koppolu Pranathi, 1st year junior resident Department of General Medicine, Government general hospital Kakinada, Andhra Pradesh India Drpranathi.koppolu@gmail.com
This article was originally published by Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd. and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Abstract
Rheumatic fever (RF) and rheumatic valvular disease remain prevalent and are still significant health hazards in developing nations. Hoarseness of voice, although a common symptom in ENT, is a rare finding in cardiac patients. However, hoarseness of voice due to recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis is an infrequent finding secondary to mitral stenosis. This case illustrates an unusual presentation of rheumatic heart disease (RHD) in young women. This case report highlights the importance of early reporting and diagnosis of RHD-RF, being very prevalent in developing nations and yet neglected.
Keywords
Ortner's Syndrome
rare cardiovocal hoarseness
Introduction
Mitral stenosis is a valvular lesion that frequently occurs due to rheumatic etiology. When untreated, it leads to left atrial enlargement, atrial fibrillation, and seemingly significantly life-threatening complications, including cardioembolic stroke.
Left vocal cord palsy and dysphagia are rare complications that we encounter.
This complication is rare these days, as intervention is done early during its course. Cardiovocal syndrome/Ortner's syndrome is hoarseness due to left recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) palsy, caused by its compression by enlarged cardiovascular structures. The cardiovocal syndrome was first discovered in 1897 by Norbert Ortner, a German physician, in three patients with severe mitral stenosis. He explained that hoarseness was due to left RLN compaction by a dilated left atrium. Many authors found mitral valve disease is the cause for 0.6 to 5% of cases of RLN paralysis. There are various diagnostic techniques for diagnosing left RLN palsy, such as neck CT and MRI, to determine the cause of nerve palsy. Untimely recognition and treatment, in addition to removal of an underlying cause, can bring change to an otherwise poor prognosis of this condition. Here, we will glimpse a case report of Ortner's syndrome in chronic rheumatic heart disease (RHD) in young women.
Case Report
An 18-year-old girl who was a known case of chronic RHD presented with complaints of hoarseness of voice for 3 months, shortness of breath for 3 months, palpitations for 15 days, and dry cough for 10 days. On examination, the heart rate is approximately 90 beats per minute with everyday pressures. We could hear a loud first heart sound in the mitral area with tachycardia along with some irregular rhythms, and listened to an audible pulmonary component of the second heart sound in the pulmonary area on auscultation. A sustained heave on palpation in the left parasternal area was present. The tapping apex was felt in the fifth intercostal space 2 cm lateral to the midclavicular line that lifts the stethoscope. I could feel an apical beat, even in the interscapular region.
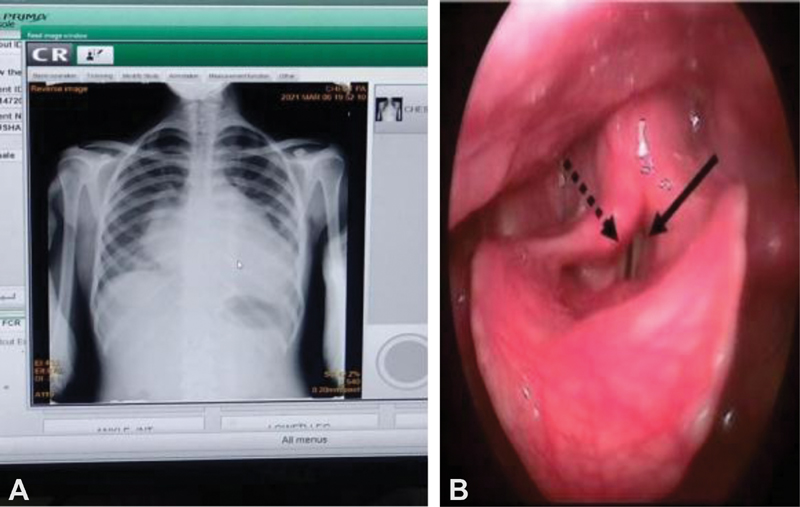
Chest X-ray Poster Anterior View Showed Cardiomegaly
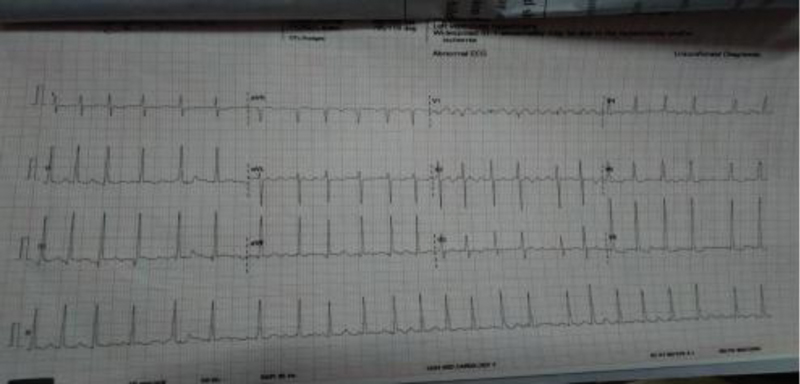
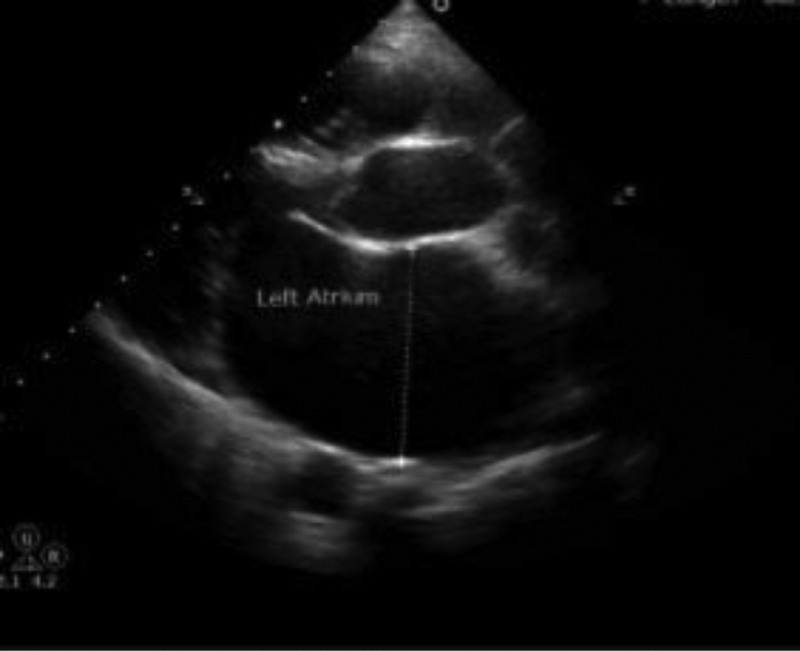
Electrocardiogram showed right axis deviation with atrial fibrillation. Two-dimension and M mode echo showed dilated left atrium of 5.2 cm, with severe mitral stenosis, chronic RHD along with mild tricuspid regurgitation. Video laryngoscopy showed paralyzed left vocal cord in a paramedian location (Figs. 1 2 3).
-
Fig. 1 Chest X-ray posteroanterior (PA) view showing cardiomegaly (A) It is the image of video laryngoscopy showing paralyzed left vocal cord (in dark black line), and compensatory movement of right vocal cord (black broken line) during adduction (B).
Fig. 1 Chest X-ray posteroanterior (PA) view showing cardiomegaly (A) It is the image of video laryngoscopy showing paralyzed left vocal cord (in dark black line), and compensatory movement of right vocal cord (black broken line) during adduction (B).
-
Fig. 2 ECG image showing atrial fibrillation.
Fig. 2 ECG image showing atrial fibrillation.
-
Fig. 3 2D ECHO image showing left atrial enlargement.
Fig. 3 2D ECHO image showing left atrial enlargement.
Discussion
The RLN provides ipsilateral motor supply to intrinsic laryngeal muscles; it arises from the vagus nerve at different levels for the left and right side. This nerve first goes down into the thorax before emerging between the trachea and esophagus to reach the neck. The right RLN arises from the level of the right subclavian artery. It takes a turn around this artery, while the course of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve is longer. It arises from the vagus nerve at the plane of the transverse aortic arch; then, it hooks below an arch of the aorta, posterior to the ligamentous arteriosus, before it enters between the trachea and esophagus, because left RLN has a long course and is more prone to damage. Injury to one side of the nerve causes hoarseness, while injury on both sides causes more severe symptoms. Various causes like birth trauma, congenital anomalies of great vessels or heart, malignant or less often benign tumors, thyroid, and cervical surgeries, endotracheal intubation, inflammation or postradiation fibrosis, organophosphorus poisoning, diabetic neuropathy, myasthenia gravis, and neurodegenerative disorders such as poliomyelitis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis can cause RLN palsy, while left RLN injury is likely due to aortic aneurysm, bronchogenic carcinoma, cervical lymphadenopathy, and enlarged left atrium. Here, in Ortner's syndrome, damage to the left RLN is due to compression of the nerve between the aorta and dilated pulmonary artery, which is the most vulnerable space for compaction. The most important part of the management is early diagnosis of the cause for left RLN palsy because the prognosis depends on the duration of the injury. In Ortner's syndrome, it is essential to treat the underlying cardiovascular condition or vascular anomaly for a successful outcome.
If symptoms are critical and the patient is not compliant with the medical treatment, then voice therapy, sometimes surgical tightening of the vocal cord, should be considered. In our case, we are following the case for mitral valve replacement for severe mitral stenosis.
Conclusion
Ortner's syndrome, also known as cardiovocal syndrome or cardiovocal hoarseness, is an infrequent condition, which can be secondary to various cardiopulmonary disorders. Hence, it would be relevant to look beyond the larynx for a case of vocal cord palsy in the patient presenting with a complaint of hoarseness of voice, especially if there is a significant history of heart disease, and perform indirect laryngoscopy if possible.
Conflict of Interest
None declared.







