Translate this page into:
Myocardial Infarction or Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy? A Case Report of a Rare Clinical Dilemma in the Setting of Atrial Myxoma
Sasinthar Rangasamy MD, DM Vadamalayan Hospitals, Madurai, Tamil Nadu 625002 India sasinthar87@gmail.com
This article was originally published by Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd. and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Abstract
Background Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) secondary to coronary embolization is one of the rare complications of atrial myxoma. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TCM), a close mimic of AMI, is extremely rare in the setting of atrial myxoma. We report a patient with atrial myxoma presenting with features leading to a clinical dilemma between these two entities.
Case summary A 60-year-old woman presented with acute chest pain with ST segment elevation. Echocardiogram revealed left ventricular (LV) apical ballooning which is typical of TCM, coexisting with a fragile left atrial mass. Emergency coronary angiogram showed a hazy lesion in the circumflex ostium and an intermediate lesion in ramus without any obstruction. Surgical excision of the tumor was done due to features of recurrent coronary embolism. The histopathology examination confirmed it as a myxoma. Regional wall motion abnormalities reversed within a month and LV function normalized. Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging at follow-up suggested myocardial infarction.
Discussion TCM can occur very rarely in the setting of atrial myxoma. In a patient with atrial myxoma presenting with features of TCM, differentiating it from coronary embolization is important.
Keywords
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy
myocardial infarction
atrial myxoma
embolization
case report
Introduction
Cardiac myxomas are benign tumors typically manifesting as embolic, obstructive, or constitutional symptoms. Coronary embolization due to atrial myxoma is uncommon with an incidence of 0.06%.1 Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TCM) is acute-onset reversible cardiomyopathy typically precipitated by acute emotional or physical stress. TCM in the setting of atrial myxoma is rarely reported.2 3 4 5 Differentiating between AMI and TCM in the presence of coronary artery disease becomes challenging.6
We describe a patient with acute coronary syndrome after a stressful event in the family, associated with incidentally detected left atrial myxoma, leading to a diagnostic dilemma between TCM and AMI secondary to coronary embolization.
Case Presentation
A 60-year-old woman, suffering from hypertension and diabetes,, presented with compressive chest pain for 12 hours. She had progressive dyspnea of New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II to class III over 4 years, with paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (PND) for 3 months. A month ago, her husband had died. On examination, there was a loud first heart sound and an intermittent low-pitched early diastolic sound followed by a mid-diastolic rumble.
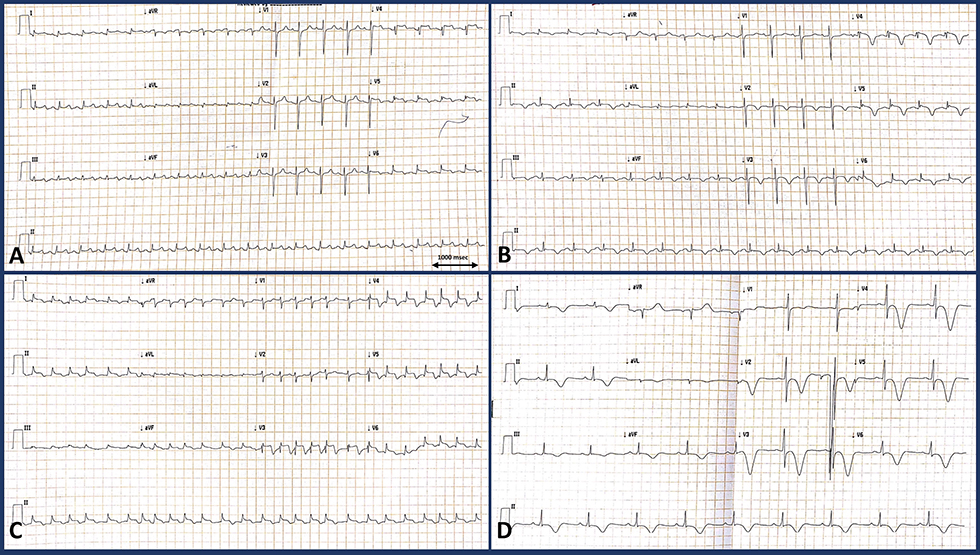
Electrocardiogram (ECG) showed ST elevation in inferolateral leads (Fig. 1). Peak troponin I was175 ng/L. Other routine investigations were insignificant.
-
Fig. 1 [MC8]Electrocardiogram of the patient at different timelines. (a) (At presentation, day 1) Sinus tachycardia at 100 bpm with ST segment elevations in leads V4–V6, I, aVL, II, III, and aVF with biphasic T wave inversions and ST segment depression in lead aVR. (b) (Day 2) Sinus rhythm at 90 bpm with new onset deep T inversions in leads V2-V6, I, avL, II, III, and avF with minimal ST elevations in leads V4–V6, I, aVL. (c) (Postoperative) Atrial fibrillation with fast ventricular rate with persistent ST elevations in V3–V6, I, aVL, II, III, and aVF. (d) Follow-up ECG 1 month later showing sinus rhythm at 60 bpm, no pathological Q waves, symmetrical deep T inversions in V2–V6, II, III, avL, and I with QTc interval prolongation.
Fig. 1 [MC8]Electrocardiogram of the patient at different timelines. (a) (At presentation, day 1) Sinus tachycardia at 100 bpm with ST segment elevations in leads V4–V6, I, aVL, II, III, and aVF with biphasic T wave inversions and ST segment depression in lead aVR. (b) (Day 2) Sinus rhythm at 90 bpm with new onset deep T inversions in leads V2-V6, I, avL, II, III, and avF with minimal ST elevations in leads V4–V6, I, aVL. (c) (Postoperative) Atrial fibrillation with fast ventricular rate with persistent ST elevations in V3–V6, I, aVL, II, III, and aVF. (d) Follow-up ECG 1 month later showing sinus rhythm at 60 bpm, no pathological Q waves, symmetrical deep T inversions in V2–V6, II, III, avL, and I with QTc interval prolongation.
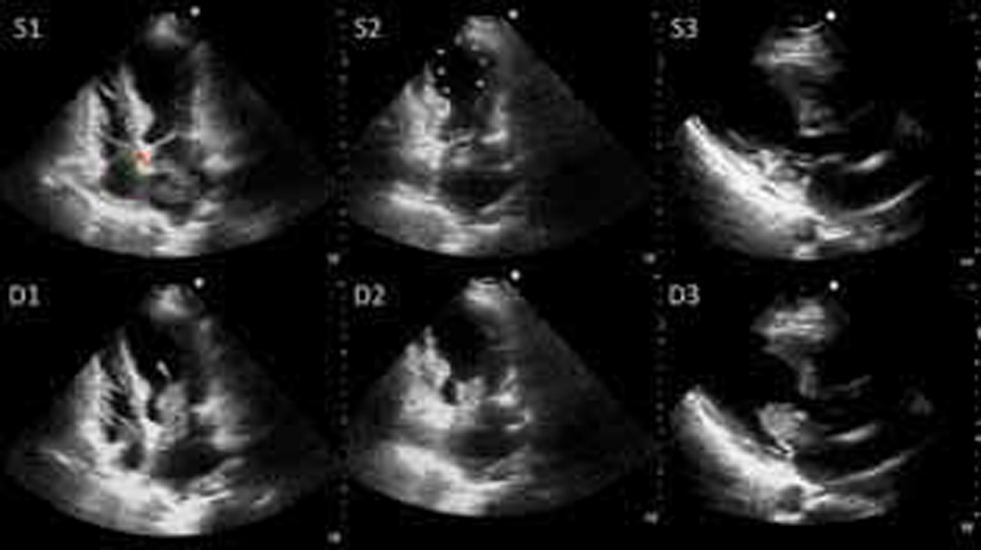
A bedside two-dimensional (2D) transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) (Fig. 2) showed regional wall motion abnormality (RWMA) causing left ventricular (LV) systolic apical ballooning typical of TCM (Supplementary Videos 1 –3). Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 38%. There was a large polypoid friable left atrial mass of size 51 mm × 28 mm, attached to the fossa ovalis.
-
Fig. 2
Transthoracic echocardiogram still frame images at presentation. Upper panels (S1, S2, and S3): Systolic frames in apical four-chamber, apical two-chamber, and parasternal long axis views showing regional wall motion abnormalities causing LV apical ballooning (yellow arrowheads) with hyperkinetic LV base. Note the friable pedunculated mass in the left atrium with attachment to the interatrial septum (red arrowhead). Lower panels (D1, D2, and D3): Diastolic frames in apical four-chamber, apical two-chamber, and parasternal long axis views showing the mass prolapsing into the LV obstructing the mitral inflow (blue arrowhead).
Fig. 2 Transthoracic echocardiogram still frame images at presentation. Upper panels (S1, S2, and S3): Systolic frames in apical four-chamber, apical two-chamber, and parasternal long axis views showing regional wall motion abnormalities causing LV apical ballooning (yellow arrowheads) with hyperkinetic LV base. Note the friable pedunculated mass in the left atrium with attachment to the interatrial septum (red arrowhead). Lower panels (D1, D2, and D3): Diastolic frames in apical four-chamber, apical two-chamber, and parasternal long axis views showing the mass prolapsing into the LV obstructing the mitral inflow (blue arrowhead).
An emergency coronary angiogram (CAG) revealed nonobstructive coronaries and TIMI III flow. She was put on conservative management following which chest pain improved.
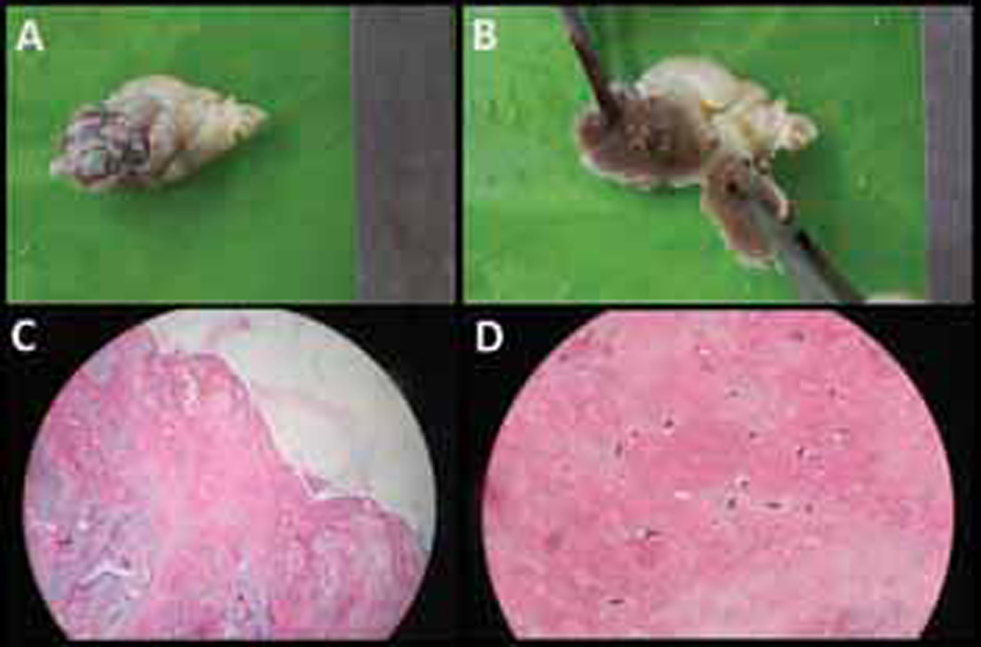
The next day she developed recurrent chest pain associated with fresh T wave inversion in the anterior leads. Suspecting recurrent embolic showers, she was taken up for emergency surgical excision of atrial myxoma. A soft friable mass of ~40 mm × 30 mm was excised in toto. Patient’s clinical condition improved, and she was extubated. A TTE done before discharge showed significant improvement of RWMA with an LVEF of 45%. The histopathological examination of the resected tumor confirmed the diagnosis of atrial myxoma (Fig. 3).
-
Fig. 3 (a,b) Gross pathology of the left atrial myxoma showing yellowish, irregular, soft, friable mass. (c,d) Histopathology showing spindle-shaped cells embedded in abundant extracellular matrix consistent with benign atrial myxoma. (H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; panel c: 40× and panel d 100× magnification).
Fig. 3 (a,b) Gross pathology of the left atrial myxoma showing yellowish, irregular, soft, friable mass. (c,d) Histopathology showing spindle-shaped cells embedded in abundant extracellular matrix consistent with benign atrial myxoma. (H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; panel c: 40× and panel d 100× magnification).
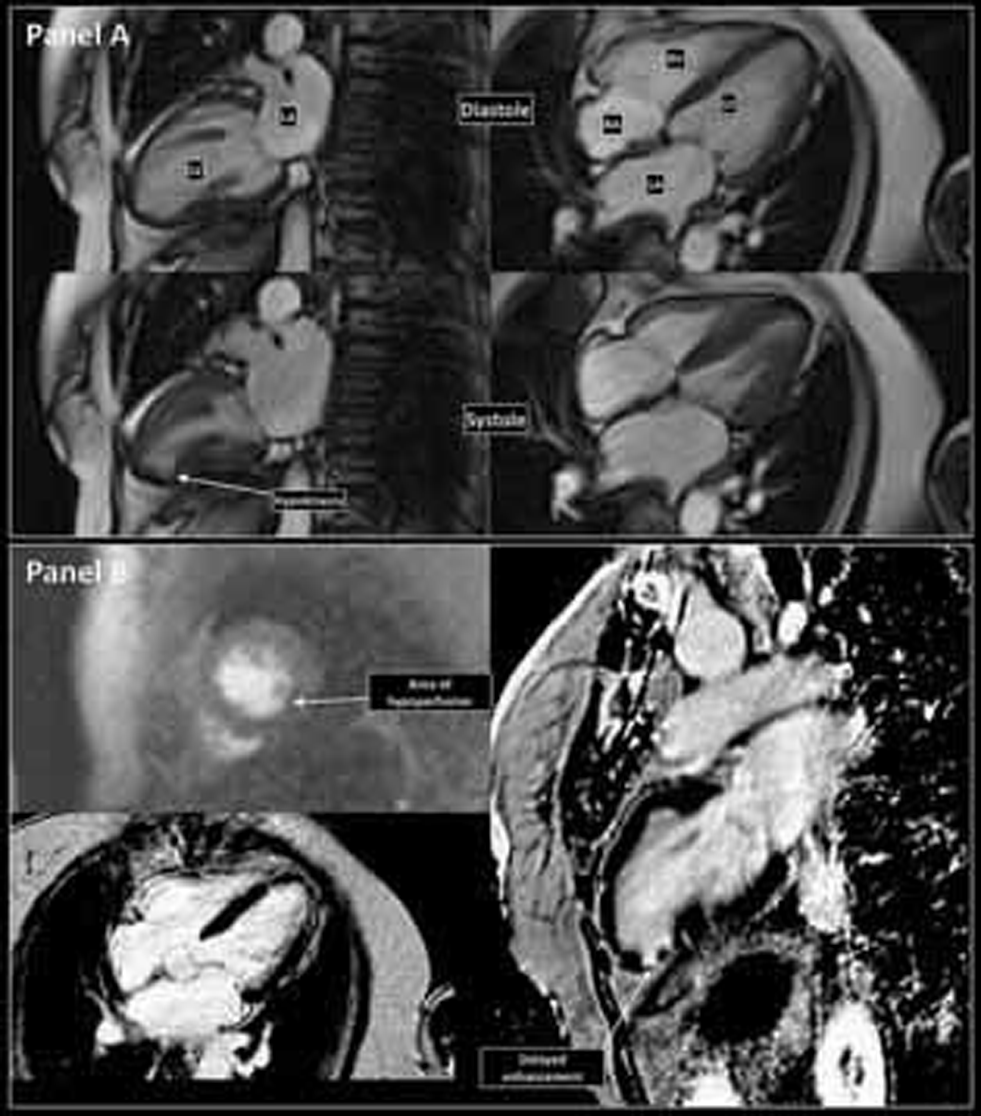
At 1-month follow-up, LV function normalized and no RWMA was detectable by echocardiogram. A cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging done at 3 months (Fig. 4) showed normal LVEF (65%), RWMA of inferior and inferolateral wall of the LV apex, and a small area of impaired perfusion with late gadolinium enhancement (LGE), suggesting that the past event was not only stress cardiomyopathy but there was also a vascular event. The patient was free of dyspnea or angina on further follow-up.
-
Fig. 4
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging at 3 months follow-up. (a) Diastolic (top row) and systolic (bottom row) frames of true FISP “bright blood” images of the heart showing failure of systolic thickening of apical inferior wall suggestive of regional wall motion abnormality. (b) Top left: Dynamic gadolinium enhanced myocardial perfusion imaging showing a small area of impaired perfusion at the hypokinetic region. Bottom left: 4-chamber T2-weighted spin echo image shows no evidence of myocardial edema. Right: Delayed images obtained shows bright subendocardial LGE involving apical inferior and inferolateral wall suggestive of scar.
Fig. 4 Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging at 3 months follow-up. (a) Diastolic (top row) and systolic (bottom row) frames of true FISP “bright blood” images of the heart showing failure of systolic thickening of apical inferior wall suggestive of regional wall motion abnormality. (b) Top left: Dynamic gadolinium enhanced myocardial perfusion imaging showing a small area of impaired perfusion at the hypokinetic region. Bottom left: 4-chamber T2-weighted spin echo image shows no evidence of myocardial edema. Right: Delayed images obtained shows bright subendocardial LGE involving apical inferior and inferolateral wall suggestive of scar.
Discussion
Atrial myxoma presenting with embolization is regarded as a “surgical emergency” because risk of recurrent embolization increases with time.7
TCM usually occurs in postmenopausal women typically following physical or emotional stress. Death of a loved one and exacerbation of a chronic medical condition (atrial myxoma) might be the potential triggers in our patient. TCM can mimic AMI and is characterized by LV systolic apical ballooning.8 There are only few cases of TCM reported in the setting of LA myxoma.2 3 4 5 9
Differentiating TCM from AMI based on history, clinical examination, ECG, and cardiac enzymes can be difficult.10 The troponin-ejection fraction product (TEFP) is 665 (peak troponin I 17.5 ng/dL × LVEF 38%) which is slightly high and also CK-Mb was slightly higher too, favoring AMI.11 Whereas the InterTAK diagnostic score is 74 (Table 1), indicating a high probability of TCM.12 LV apical ballooning in TTE can also be seen in occlusion of a wraparound LAD or when showers of myocardial embolization involves multiple coronary artery territories.13NT PRO BNP levels were marginally elevated and it could be explained by failure secondary to LV dysfunction which occur in both AMI and TCM. CAD can coexist in ~15% cases of TCM.8 So both the modified Mayo Clinic diagnostic criteria and the InterTAK diagnostic criteria for TCM allow the presence of concurrent CAD.14 15
|
S. No. |
Clinical variables |
Maximum points |
Patient’s points |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Female gender |
25 |
25 |
|
2 |
Emotional stress |
24 |
24 |
|
3 |
Physical stress |
13 |
13 |
|
4 |
No ST-segment depression |
12 |
12 |
|
5 |
Acute, former, or chronic psychiatric disorder |
11 |
0 |
|
6 |
Acute, former, or chronic neurological disorder |
9 |
0 |
|
7 |
Prolonged QTc time (female > 460 ms; male > 440 ms) |
6 |
0 |
|
Total score |
100 |
74 (92.9% probability of Takotsubo) |
Also, TCM and acute STEMI can rarely occur concurrently.16 CMR is increasingly recognized as a modality of choice to differentiate TCM from AMI in doubtful cases. TCM usually does not show LGE or when it is there it is usually less dense, whereas bright LGE is frequent in AMI.17
Evidences in favor of TCM in this case were gender, age group, presence of a definite emotional and physical trigger, characteristic echocardiographic features, a higher InterTAK diagnostic score, absence of obstructive coronary lesions in angiogram and also not correlating with RWMA, disproportionately low cardiac enzymes, echocardiographic complete resolution of RWMA, and normalization of LV function within a month without any coronary intervention. Evidences favoring myocardial embolization are the presence of underlying myxoma with high-risk features, temporal course of the disease, the hazy lesion in LCX ostium, recurrent chest pain with fresh ECG changes, and persistent bright LGE in CMR.
Even if embolization has occurred, the features satisfy the current diagnostic criteria for TCM.14 But it has to be understood that myocardial embolization and TCM are two distinct entities with different management strategies even though both can rarely coexist.16 Differentiating between these two is important because in case of embolization, early excision of the tumor could prevent recurrence and in turn decrease further morbidity and mortality. But in atrial myxoma associated with TCM, emergency surgery may not be mandatory. It would be prudent to wait until the LV function recovers. Several case reports raise the question of possible association between these two conditions2 3 45 9
Follow-up CMR confirmed this as a case of TCM occurring concurrently with AMI due to coronary embolization from atrial myxoma.
Conclusion
The following conclusions can be drawn from this case:
-
Atrial myxoma is one of the rare nonatherosclerotic causes of acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
-
A high index of suspicion is needed to diagnose myxoma in the setting of AMI as surgery is the only definitive treatment that improves prognosis. 2D echocardiography, preferably done before revascularization, helps to diagnose this condition and guide treatment properly.
-
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TCM) can occur very rarely in the setting of atrial myxoma.
-
In a patient with atrial myxoma presenting with features of TCM, differentiating it from myocardial embolization is crucial in guiding management decisions. CMR, both in acute setting and at follow-up, helps in making a definitive diagnosis. NT PRO BNP levels may be elevated in both the cases secondary to failure.
-
Rarely, TCM can coexist with AMI. InterTAK diagnostic score can help in the diagnosis of TCM.
Conflict of Interest
None declared.
Statement of Consent
The authors confirm that written consent for submission and publication of this case report including image(s) and associated text has been obtained from the patient.
Disclosure of Funding None.
References
- Left atrial myxoma presenting with myocardial infarction. Case report and review of the literature. Int J Cardiol. 1997;62(01):73-75.
- [Google Scholar]
- Three dimensional echocardiography of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy with atrial myxoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2010;2010:2010.
- [Google Scholar]
- ‘A blessing in disguise’: myxoma cordis and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(15):914.
- [Google Scholar]
- Multiregional embolizations and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy associated with left atrial myxoma. Ann ThoracCardiovascSurg. 2012;18(06):577-581.
- [Google Scholar]
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for Takotsubo syndrome and long QT after cardiac surgery. Med Intensiva. 2017;41(07):441-443.
- [Google Scholar]
- Acute coronary syndrome or Takotsubo cardiomyopathy: the suspect may not always be the culprit. Int J Cardiol. 2015;187:116-119.
- [Google Scholar]
- Eleven years’ experience with Korean cardiac myxoma patients: focus on embolic complications. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;33(05):471-479.
- [Google Scholar]
- Clinical features and outcomes of Takotsubo (stress) cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(10):929-938.
- [Google Scholar]
- Takotsubo cardiomyopathy with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) requirement after atrial myxoma surgery. Int J Cardiovasc Sci. 2017;30:277-280.
- [Google Scholar]
- Takotsubo cardiomyopathy: a unique cardiomyopathy with variable ventricular morphology. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010;3(06):641-649.
- [Google Scholar]
- Usefulness of the troponin-ejection fraction product to differentiate stress cardiomyopathy from ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2014;113(03):429-433.
- [Google Scholar]
- A novel clinical score (InterTAK Diagnostic Score) to differentiate Takotsubo syndrome from acute coronary syndrome: results from the International Takotsubo Registry. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017;19(08):1036-1042.
- [Google Scholar]
- Electrocardiographic differential diagnosis between Takotsubo syndrome and distal occlusion of LAD is not easy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56(19):1610-1611.
- [Google Scholar]
- Apical ballooning syndrome (Takotsubo or stress cardiomyopathy): a mimic of acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 2008;155(03):408-417.
- [Google Scholar]
- International expert consensus document on Takotsubo syndrome (part II): diagnostic workup, outcome, and management. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(22):2047-2062.
- [Google Scholar]
- Apical ballooning (Takotsubo) syndrome with concurrent ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017:2017.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cardiac magnetic resonance assessment of takotsubo cardiomyopathy. ClinRadiol. 2016;71(01):e110-e119.
- [Google Scholar]








